Preventive Measures Against Tropical Diseases
Preventing tropical diseases is crucial for travelers planning to visit these sensitive regions. It is recommended to follow effective preventive measures to reduce the risk of contracting infectious diseases. This includes receiving recommended vaccinations before traveling, with a focus on vaccines that protect against prevalent diseases in tropical areas. The use of mosquito repellents, such as sprays and creams, is essential to avoid mosquito-borne illnesses. It is also highly advised to avoid consuming untreated water and to eat clean food, with regular handwashing. Adhering to local health guidelines and medical advice plays a significant role in enhancing effective prevention and ensuring the safety of travelers in these areas.
Preventing tropical diseases is a vital aspect of travelers' preparedness and maintaining their health during visits to these sensitive regions. Receiving vaccinations is essential to boost immunity against diseases prevalent in tropical areas, and it is advisable to do this well before traveling. On the other hand, the use of mosquito repellents plays a crucial role in preventing diseases transmitted through mosquito bites. Travelers should also adhere to personal hygiene guidelines and be cautious about avoiding untreated water consumption and consuming clean food. Adhering to these preventive measures enhances health protection effectiveness and helps reduce the risk of contracting diseases in these tropical regions.
The First Step to Health Protection
Traveling to tropical destinations can be an exciting adventure, but it comes with potential health risks due to exposure to tropical diseases. Getting the right tropical vaccinations is the first and crucial step to protect your health during such journeys. Here's a detailed exploration of the importance and considerations related to tropical vaccinations:
1. Understanding Tropical Diseases:
-
Disease Exposure Risk: Tropical regions are known for harboring specific diseases that may not be prevalent in other parts of the world. These diseases include malaria, yellow fever, dengue fever, typhoid, and others. Understanding the risks associated with these diseases is essential for travelers.
-
Local Health Recommendations: Researching and understanding the health recommendations for the specific tropical destination is crucial. Local health authorities and travel clinics provide valuable information on prevalent diseases and required vaccinations.
2. Importance of Tropical Vaccinations:
-
Disease Prevention: The primary goal of tropical vaccinations is to prevent the contraction of potentially serious diseases. Vaccinations stimulate the immune system to create protection against specific pathogens, reducing the risk of infection.
-
Public Health Protection: Tropical vaccinations not only safeguard individuals but also contribute to public health. By preventing the spread of diseases, especially those with the potential for outbreaks, vaccinations play a role in maintaining community health.
3. Common Tropical Vaccinations:
-
Yellow Fever Vaccine: Required for entry into certain tropical countries, the yellow fever vaccine provides protection against the yellow fever virus transmitted by mosquitoes.
-
Malaria Prophylaxis: While not a vaccine, malaria prophylaxis involves taking medication to prevent malaria infection. The choice of medication depends on the specific region and the type of malaria present.
-
Typhoid Vaccine: Typhoid is a bacterial infection, and vaccination is recommended for travelers to areas with poor sanitation and water quality.
-
Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: These vaccines protect against viral infections affecting the liver, and they are often recommended for travelers to tropical regions.
4. Vaccination Timing and Planning:
-
Advance Planning: Some vaccinations may require multiple doses or take time to become effective. It's crucial to plan well in advance of the travel date to ensure full immunity.
-
Routine Vaccinations: In addition to tropical-specific vaccinations, ensuring that routine vaccinations (such as measles, mumps, rubella, and influenza) are up-to-date is important for overall health protection.
5. Consulting a Healthcare Professional:
-
Travel Health Clinics: Healthcare professionals specializing in travel medicine can provide personalized advice based on the traveler's health history, destination, and planned activities.
-
Individual Health Assessment: An individual health assessment takes into account factors such as age, existing health conditions, and previous vaccination history to determine the most suitable vaccination plan.
6. Additional Health Precautions:
-
Mosquito Protection: In addition to vaccinations, using mosquito repellent, wearing long sleeves and pants, and using bed nets contribute to protection against diseases like malaria and dengue.
-
Food and Water Safety: Adhering to safe food and water practices is essential in preventing gastrointestinal infections. This includes avoiding consuming raw or undercooked food and using bottled or purified water.
Tropical vaccinations are a critical aspect of ensuring health protection for travelers venturing into tropical regions. Understanding the specific health risks, getting the necessary vaccinations, and adopting additional preventive measures contribute to a safer and healthier travel experience. Consulting with healthcare professionals and staying informed about the latest health recommendations for the destination are key components of responsible travel planning.
Effective Defense Against Transmitting Diseases
Mosquitoes are not only annoying pests but also carriers of various diseases that can have serious health implications for humans. Implementing effective mosquito control measures is crucial to safeguard against the transmission of diseases. Here's a detailed exploration of mosquito control methods and their importance:
1. Understanding Mosquito-Borne Diseases:
-
Disease Transmission: Mosquitoes are vectors for diseases caused by parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Common mosquito-borne diseases include malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and chikungunya.
-
Global Health Impact: Mosquito-borne diseases have a significant impact on global health, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Malaria alone is responsible for a substantial number of annual deaths worldwide.
2. Importance of Mosquito Control:
-
Disease Prevention: The primary goal of mosquito control is to prevent the transmission of diseases from mosquitoes to humans. By reducing mosquito populations and limiting their access to humans, the risk of disease transmission can be significantly lowered.
-
Public Health Impact: Mosquito control measures contribute to public health by preventing outbreaks of diseases. This is particularly crucial in regions where mosquito-borne diseases are endemic.
3. Effective Mosquito Control Methods:
-
Source Reduction: Eliminating or reducing mosquito breeding sites is a fundamental approach. This includes removing stagnant water in containers, cleaning gutters, and properly maintaining water storage areas.
-
Biological Control: Introducing natural predators of mosquitoes, such as certain fish species or larvivorous insects, can help control mosquito populations in aquatic habitats.
-
Insecticides: The targeted use of insecticides can be effective in reducing adult mosquito populations. This may involve the use of insecticide-treated bed nets, indoor residual spraying, or fogging in outdoor areas.
-
Mosquito Traps: Various types of traps are available, including those that use attractants or carbon dioxide to lure mosquitoes. These traps can be useful in reducing local mosquito numbers.
-
Genetic Control: Emerging technologies, such as the release of genetically modified mosquitoes, aim to reduce mosquito populations by interfering with their ability to reproduce.
4. Personal Protection Measures:
-
Mosquito Repellents: The use of insect repellents on exposed skin and clothing provides personal protection against mosquito bites. Repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus are commonly recommended.
-
Protective Clothing: Wearing long sleeves, long pants, and socks can help minimize exposed skin, reducing the risk of mosquito bites.
-
Bed Nets: In areas where mosquito-borne diseases are prevalent, the use of insecticide-treated bed nets is an effective way to protect individuals, especially during sleep.
-
Avoiding Peak Mosquito Activity: Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk. Avoiding outdoor activities during these times can reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
5. Community Engagement and Education:
-
Community Clean-Up Campaigns: Involving communities in efforts to eliminate mosquito breeding sites through clean-up campaigns can be impactful.
-
Educational Programs: Raising awareness about mosquito-borne diseases, their transmission, and preventive measures is essential. This can empower communities to actively participate in mosquito control.
Mosquito control is a vital component of public health strategies, especially in regions where mosquito-borne diseases pose a significant threat. Implementing a combination of source reduction, biological control, insecticides, personal protection measures, and community engagement can effectively reduce the risk of disease transmission. A comprehensive approach that involves individuals, communities, and public health authorities is key to achieving successful mosquito control and mitigating the impact of mosquito-borne diseases.
A Guide to Safe Travel
Traveling to tropical regions offers exciting adventures, but it also comes with unique challenges related to personal hygiene. Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial to prevent health issues and ensure a safe and enjoyable journey. Here's a detailed guide on personal hygiene in tropical regions:
1. Water Safety:
-
Safe Drinking Water: In many tropical areas, access to safe drinking water may be a concern. Avoid drinking tap water unless it has been properly treated or boiled. Opt for bottled water from reputable sources.
-
Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential, especially in hot and humid climates. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and carry a reusable water bottle. Be cautious of dehydration, as it can lead to various health issues.
2. Food Safety:
-
Avoid Street Food Risks: While street food can be tempting, it may pose a risk of foodborne illnesses. Choose reputable eateries, ensure food is cooked thoroughly, and opt for hot, freshly prepared meals.
-
Wash Fruits and Vegetables: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with safe water before consumption. Peel when necessary, and avoid raw or undercooked seafood to prevent contamination.
3. Personal Hygiene Practices:
-
Hand Hygiene: Regular handwashing is crucial to prevent the spread of infections. Use soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, especially before eating or after using public facilities.
-
Showering and Bathing: Shower regularly to remove sweat, dirt, and bacteria. Use clean and safe water for bathing. In areas where water quality is questionable, consider using wet wipes or no-rinse body wipes.
-
Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth with bottled or treated water. Avoid using tap water for brushing to prevent exposure to contaminants.
4. Insect Bite Prevention:
-
Mosquito Protection: Tropical regions often harbor disease-carrying mosquitoes. Use insect repellent containing DEET, wear long sleeves and pants, and sleep under a mosquito net if necessary. Consider clothing treated with insect repellent.
-
Avoiding Infections: Prevent infections from insect bites by keeping wounds clean and covered. Apply antiseptic creams to bites and scratches promptly.
5. Clothing Choices:
-
Light and Breathable Fabrics: Choose lightweight, breathable fabrics to stay cool and comfortable. Long-sleeved shirts and pants can provide additional protection against the sun and insects.
-
Foot Hygiene: Keep your feet clean and dry, as damp conditions can lead to fungal infections. Wear breathable footwear and change socks regularly, especially if they become wet.
6. Sun Protection:
-
Use Sunscreen: Protect your skin from harmful UV rays by using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Reapply sunscreen every few hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
-
Cover Up: Wear hats, sunglasses, and lightweight clothing to shield yourself from the sun. Seek shade during peak sunlight hours to reduce the risk of sunburn.
7. Medical Precautions:
-
Vaccinations: Check with healthcare professionals for recommended vaccinations before traveling to tropical regions. Ensure routine vaccinations are up-to-date, and consider specific vaccinations based on your destination.
-
Travel Health Insurance: It's advisable to have travel health insurance that covers medical expenses and emergency evacuations. Familiarize yourself with local healthcare facilities and emergency contact information.
Maintaining personal hygiene in tropical regions is essential for a safe and enjoyable travel experience. By prioritizing water and food safety, practicing good personal hygiene habits, protecting against insect bites, choosing appropriate clothing, and taking necessary medical precautions, travelers can reduce the risk of health issues and fully embrace the wonders of tropical destinations. Safe and healthy travels!
Avoiding Untreated Water Consumption
Consuming untreated water poses significant health risks, especially in regions where water quality may be questionable. To ensure your health and well-being during travel or in areas with compromised water safety, it's crucial to adopt strategies for avoiding untreated water consumption. Here's a detailed guide on maintaining health by steering clear of untreated water:
1. Safe Drinking Water Sources:
-
Bottled Water: Opt for commercially bottled water from reputable brands. Ensure that the seal is intact and unbroken. Bottled water is often treated and considered safe for consumption.
-
Boiled or Treated Water: If bottled water is unavailable, boil tap water for at least one minute to kill harmful microorganisms. Alternatively, use water purification tablets or filters designed for microbial removal.
2. Avoiding Ice and Beverages:
-
No Ice in Drinks: In regions with uncertain water quality, avoid ice in beverages as it may be made from untreated water. Confirm that any ice used has been produced from safe and treated water sources.
-
Choose Bottled or Boiled Beverages: Opt for bottled or beverages made with boiled water. This precaution extends to hot drinks like tea or coffee, ensuring that the water used in their preparation is safe.
3. Cautious Food Choices:
-
Freshly Cooked and Hot Meals: Prefer freshly cooked and hot meals, as the cooking process can kill harmful bacteria and parasites. Avoid raw or undercooked food, especially seafood, to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
-
Selecting Reputable Establishments: Choose restaurants and eateries with good hygiene practices. Reputable establishments are more likely to use treated water in food preparation.
4. Personal Water Treatment:
-
Water Purification Tablets: Carry water purification tablets containing chlorine, iodine, or other disinfectants. Follow the instructions provided to treat water before consumption.
-
Portable Water Filters: Use portable water filters designed for travel. These filters can effectively remove contaminants, providing you with a safe water source.
5. Hydration Awareness:
-
Regular Hydration: Ensure you stay adequately hydrated, especially in hot and humid climates. Carry a reusable water bottle and refill it from known safe sources. Dehydration can lead to various health issues.
-
Recognize Dehydration Symptoms: Familiarize yourself with symptoms of dehydration, such as dizziness, dark urine, or excessive thirst. Seek medical attention if signs of dehydration appear.
6. Educate Yourself on Local Water Conditions:
-
Research Water Quality: Before traveling to a new destination, research the local water conditions. Be aware of any waterborne diseases prevalent in the region and take necessary precautions.
-
Ask Locals or Accommodation Staff: Seek information from locals or your accommodation staff about the safety of the local water supply. They can provide valuable insights and guidance.
7. Emergency Preparedness:
-
Carry a Water Purification Device: Include a compact water purification device in your travel essentials. This ensures that you have a backup option in case you encounter untreated water unexpectedly.
-
Know Local Medical Facilities: Familiarize yourself with the location of local medical facilities in case you need prompt medical attention due to waterborne illnesses.
Avoiding untreated water consumption is paramount for maintaining health while traveling or residing in regions with questionable water quality. By adopting these strategies, including opting for safe water sources, being cautious with food and beverages, treating water when necessary, and staying informed about local conditions, you can safeguard yourself from waterborne diseases and enjoy a healthy journey. Prioritize your health by making informed choices regarding water consumption.
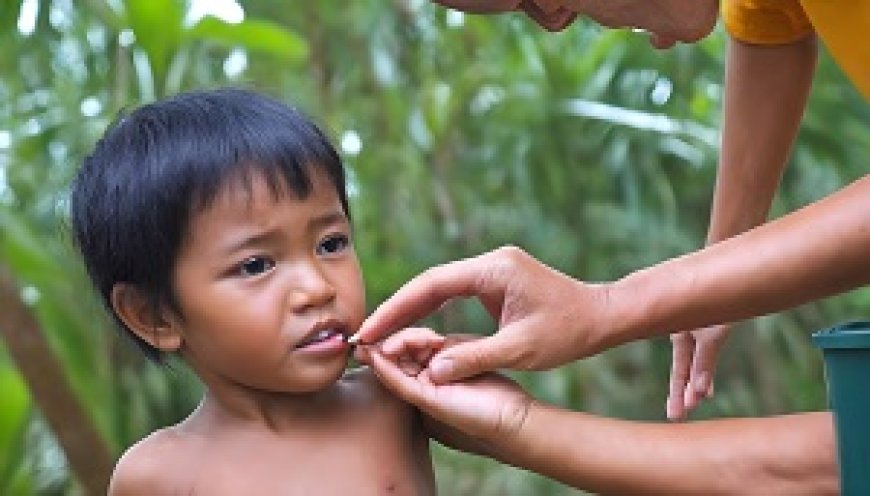
Mitigating Disease Spread in Tropical Areas
Child vaccination is a critical component of public health efforts, especially in tropical areas where the risk of infectious diseases is often heightened. Mitigating the spread of diseases in these regions requires a comprehensive and proactive approach to ensure the well-being of children. Here's a detailed guide on the importance of child vaccination and its role in mitigating disease spread in tropical areas:
1. Importance of Child Vaccination:
-
Disease Prevention: Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent various infectious diseases that can have severe consequences for children. It helps the immune system recognize and fight specific pathogens, reducing the risk of infection.
-
Community Immunity: Child vaccination contributes to the concept of herd immunity. When a significant portion of the population is immunized, it creates a protective barrier, making it harder for diseases to spread within the community, thus safeguarding those who may be more vulnerable.
-
Eradication of Diseases: Successful vaccination campaigns have led to the eradication or significant reduction of several deadly diseases globally, showcasing the impact of widespread immunization efforts.
2. Vaccines Recommended for Tropical Areas:
-
Routine Vaccinations: Ensure children receive routine vaccinations as per the recommended schedule. This often includes vaccines for diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, and others.
-
Tropical Disease Vaccines: In tropical areas, specific vaccines may be recommended to address region-specific risks. Examples include vaccines for yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, or typhoid fever, depending on the prevalent diseases in the area.
3. Timely Vaccination Schedule:
-
Early Childhood Vaccines: Start vaccinations early in a child's life. Many vaccines are administered during infancy and early childhood to provide protection during vulnerable stages of development.
-
Adherence to Schedule: Adhere to the recommended vaccination schedule, ensuring that children receive booster shots and additional doses as required for long-term immunity.
4. Access to Vaccination Services:
-
Accessible Healthcare: Ensure that healthcare services, including vaccination clinics, are easily accessible to communities in tropical areas. This accessibility encourages parents to bring their children for timely vaccinations.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Conduct awareness campaigns to educate parents and caregivers about the importance of child vaccination, dispelling myths and addressing concerns to increase vaccination acceptance.
5. Collaboration with Health Authorities:
-
Government Initiatives: Governments and health authorities play a crucial role in implementing vaccination programs. Collaborate with these entities to establish and sustain effective vaccination campaigns in tropical regions.
-
Partnerships with NGOs: Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and international health agencies often play a role in providing vaccines and supporting vaccination initiatives. Collaborate with such organizations to enhance vaccination coverage.
6. Monitoring and Surveillance:
-
Disease Surveillance: Implement robust surveillance systems to monitor the prevalence of diseases in tropical areas. Early detection allows for swift responses, including targeted vaccination campaigns during outbreaks.
-
Monitoring Vaccine Efficacy: Continuously monitor the efficacy of vaccines used in tropical regions, considering factors such as evolving pathogens or changes in disease patterns.
Child vaccination is a cornerstone of public health strategies to mitigate the spread of diseases in tropical areas. By prioritizing routine vaccinations, addressing region-specific risks, maintaining a timely schedule, ensuring access to healthcare services, fostering collaboration with health authorities, and implementing effective monitoring systems, communities can enhance their resilience against infectious diseases. Investing in child vaccination not only protects individual children but contributes to the broader goal of creating healthier and more resilient tropical communities.
Choosing the Right Clothing to Guard Against Insect Bites
Choosing the right clothing to guard against insect bites is crucial, especially when traveling to areas where insect-borne diseases are prevalent. Proper attire not only provides physical protection but also minimizes the risk of exposure to potentially harmful insects. Here's a detailed exploration of considerations and tips for selecting the right clothing for insect bite prevention:
1. Light-Colored Clothing:
- Purpose: Light-colored clothing helps in easily spotting insects, such as mosquitoes and ticks.
- Explanation: Insects are often attracted to dark colors, so opting for light shades can make you less appealing to them.
2. Long Sleeves and Pants:
- Purpose: Covering the skin with long sleeves and pants provides a physical barrier against insect bites.
- Explanation: Exposed skin is more susceptible to bites. Wearing long clothing reduces the surface area available for insects to target.
3. Tightly Woven Fabrics:
- Purpose: Tightly woven fabrics offer better protection against smaller insects.
- Explanation: Mosquitoes and other tiny insects may have difficulty penetrating tightly woven materials. Choose clothing with a dense weave for enhanced protection.
4. Insect-Repellent Clothing:
- Purpose: Clothing treated with insect repellent provides an additional layer of defense.
- Explanation: Some fabrics are pre-treated with insect repellents like permethrin, which can deter insects. Alternatively, you can treat your clothing with insect repellent sprays.
5. Avoiding Loose Clothing:
- Purpose: Tight-fitting clothing reduces the chances of insects reaching the skin.
- Explanation: Loose clothing can create easy access points for insects. Opt for snug fits to minimize exposed areas.
6. Closed-Toe Shoes and Socks:
- Purpose: Closed-toe shoes and socks protect the feet and ankles from insect bites.
- Explanation: Insects are often found close to the ground. Covering the feet with closed shoes and socks adds an extra layer of defense.
7. Hats and Head Coverings:
- Purpose: Hats and head coverings shield the face, neck, and ears from insects.
- Explanation: These areas are commonly targeted by insects. Wearing a hat with a brim or a head covering provides added protection.
8. Permethrin-Treated Gear:
- Purpose: Treating gear like camping equipment with permethrin adds an extra layer of protection.
- Explanation: In addition to clothing, treating gear can create a bug-free zone around your belongings, reducing the risk of insect bites.
9. Clothing Layering:
- Purpose: Layering clothing allows for adaptability to varying temperatures while maintaining protection.
- Explanation: In tropical or insect-prone regions, temperature fluctuations can occur. Layering allows you to adjust your clothing while ensuring continuous coverage.
10. Clothing Inspection:
- Purpose: Regularly inspecting clothing helps identify and remove any insects.
- Explanation: Insects may land on your clothing during outdoor activities. Checking your attire allows you to promptly remove any unwanted guests.
11. Avoidance of Perfumes and Bright Colors:
- Purpose: Perfumes and bright colors can attract certain insects.
- Explanation: Insects, especially bees and wasps, may be attracted to strong scents and vibrant colors. Minimizing the use of perfumes and opting for subdued colors can help reduce attraction.
Choosing the right clothing is a fundamental aspect of insect bite prevention. By incorporating these considerations into your travel wardrobe, you can significantly reduce the risk of insect-borne diseases and enjoy a more comfortable and worry-free outdoor experience. Additionally, combining appropriate clothing with other preventive measures, such as insect repellents, further enhances your defense against bites.
Safe Eating
Safe eating is paramount when traveling to tropical regions, where specific challenges may arise in avoiding foodborne illnesses. The combination of different culinary practices, environmental conditions, and potential contamination sources makes it essential for travelers to be vigilant about their food choices. Here is a detailed exploration of the challenges and tips for safe eating in tropical regions:
1. Local Culinary Practices:
- Diverse Foods: Tropical regions often boast diverse and unique culinary offerings. While this is an exciting aspect of travel, it also means encountering unfamiliar cooking methods and ingredients.
- Street Food: Street food is a common feature in tropical destinations. While it allows a taste of local flavors, the hygiene standards may vary. Caution is advised when consuming street food.
2. Water and Ice Contamination:
- Unsafe Water Sources: Contaminated water is a primary source of foodborne illnesses. Avoid consuming raw or undercooked seafood, salads, or fruits washed in unsafe water.
- Ice Safety: Ice made from impure water can pose a risk. Opt for beverages without ice or ensure that the ice is made from purified or bottled water.
3. Hygiene Standards:
- Food Handling Practices: In some regions, there might be variations in food handling practices and hygiene standards. Look for establishments that maintain cleanliness in food preparation and service areas.
- Utensil Sanitization: Confirm that utensils and cutlery are adequately sanitized. Avoid places where hygiene practices seem questionable.
4. Seafood Safety:
- Raw Seafood Precautions: If indulging in seafood, be cautious with raw or undercooked options, as they can harbor harmful bacteria or parasites.
- Freshness Check: Choose seafood from reputable vendors and restaurants. Ensure that it looks and smells fresh.
5. Fresh Produce Handling:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Enjoying local fruits and vegetables is a part of the travel experience. Wash them thoroughly or peel them before consumption to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Avoiding Unwashed Items: Refrain from consuming raw fruits or salads from street vendors if they appear unwashed or inadequately cleaned.
6. Allergen Awareness:
- Communication with Staff: If you have food allergies, communicate clearly with restaurant staff about your dietary restrictions. Confirm ingredients and cooking methods to prevent accidental exposure to allergens.
- Translation Assistance: In areas where language might be a barrier, consider using translation apps or cards that convey your dietary needs.
7. Personal Hygiene:
- Hand Hygiene: Maintain good personal hygiene, especially before eating. Use hand sanitizers or wash hands with soap and clean water.
- Utensil Usage: If provided with utensils, ensure they are clean before using them. Consider carrying disposable wipes for additional sanitation.
8. Choosing Established Eateries:
- Reputable Restaurants: Opt for well-established and reputable restaurants. They are likely to adhere to higher hygiene standards.
- Online Reviews: Check online reviews or ask locals for recommendations to identify places with positive feedback on food safety.
9. Avoiding High-Risk Foods:
- Undercooked Meats: Minimize consumption of undercooked or raw meats, as they pose a higher risk of bacterial contamination.
- Unpasteurized Dairy: Steer clear of unpasteurized dairy products, as they can harbor harmful bacteria.
10. Traveler's Diarrhea Prevention:
- Probiotics: Consider taking probiotics before and during your trip, as they may help in preventing traveler's diarrhea.
- Safe Drinking Practices: Stick to bottled or purified water and avoid drinks with uncertain water sources.
While exploring tropical regions, enjoying the local cuisine is an integral part of the experience. However, practicing safe eating habits is crucial to avoid foodborne illnesses. Travelers should stay informed, exercise caution, and prioritize establishments with high hygiene standards to ensure a healthy and enjoyable culinary journey in tropical destinations.
Healthy Travel
Healthy travel is essential, especially when venturing into tropical areas where specific health risks may be present. To ensure a safe and enjoyable journey, individuals should take proactive measures to prevent diseases. Here are detailed tips for healthy travel to tropical areas:
1. Pre-Travel Health Consultation:
- Medical Check-Up: Schedule a pre-travel health consultation with a healthcare professional. Discuss the destination, duration of stay, and any pre-existing medical conditions.
- Vaccinations: Ensure routine vaccinations are up to date. Depending on the destination, inquire about specific vaccinations for tropical diseases.
2. Mosquito-Borne Disease Prevention:
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus to exposed skin. Reapply as directed.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Dress in long sleeves, pants, and closed shoes, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active.
- Bed Net Usage: Sleep under a treated mosquito bed net, particularly if staying in accommodations with open windows or without screens.
3. Water and Food Safety:
- Bottled or Purified Water: Consume only bottled or properly purified water. Avoid ice in drinks unless you are sure it's made from safe water.
- Safe Food Practices: Eat thoroughly cooked and hot foods. Avoid raw or undercooked seafood, unpeeled fruits, and raw vegetables unless they can be washed or peeled.
4. Medication and First Aid Kit:
- Prescription Medications: Bring an ample supply of any prescription medications, along with a copy of prescriptions.
- First Aid Kit: Pack a basic first aid kit with essentials such as bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, and any specific medications you might need.
5. Sun Protection:
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Protective Clothing: Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and lightweight, long-sleeved clothing to shield against the sun's harmful rays.
6. Stay Hydrated:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Tropical climates can lead to dehydration. Stay well-hydrated by drinking ample water throughout the day.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, as it can contribute to dehydration.
7. Respiratory Protection:
- Air Quality Awareness: Be mindful of air quality in tropical regions. In areas with poor air quality, consider wearing a mask to protect against pollutants or allergens.
- Asthma Inhaler: If you have asthma or respiratory conditions, carry necessary medications and inhalers.
8. Travel Insurance:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Invest in travel insurance that provides comprehensive coverage, including medical emergencies and evacuation.
- Policy Review: Understand the terms of your insurance policy, including coverage limits and exclusions.
9. Stay Informed About Local Health Risks:
- Health Alerts: Stay updated on health alerts and advisories for the destination. Follow local health guidelines and recommendations.
- Local Healthcare Access: Know the locations of local healthcare facilities and emergency services.
10. Cultural Sensitivity:
- Respect Local Customs: Be culturally sensitive regarding health practices. Respect local customs related to hygiene and healthcare.
- Ask for Guidance: When unsure, ask locals or seek guidance from travel authorities regarding health practices specific to the destination.
Maintaining health during travel to tropical areas involves a combination of preparation, precaution, and awareness. By following these tips, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of contracting diseases and ensure a healthier and more enjoyable travel experience. Always prioritize personal well-being and take proactive steps to safeguard health throughout the journey.
Health Risk Analysis
Health Risk Analysis in tropical regions is crucial for individuals planning to visit or reside in areas with unique environmental and biological characteristics. The tropics are known for their warm climate, high humidity, and diverse ecosystems, but they also pose specific health risks due to the prevalence of certain diseases. Understanding these risks and implementing preventive measures is essential. Here is a detailed guide to Health Risk Analysis in tropical regions:
1. Vector-Borne Diseases:
- Mosquito-Borne Diseases: In tropical regions, mosquitoes are vectors for diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and chikungunya. Implement preventive measures like using mosquito nets, wearing long sleeves, and applying insect repellents.
- Other Vectors: Be aware of other disease vectors, such as ticks and fleas, which may transmit illnesses like Lyme disease and typhus.
2. Waterborne Diseases:
- Contaminated Water Sources: Tropical regions may have issues with water sanitation. Avoid drinking untreated water and consume only properly treated or bottled water to prevent waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid, and dysentery.
- Food Safety: Ensure that food is prepared and stored in hygienic conditions to prevent contamination.
3. Tropical Infectious Diseases:
- Malaria: Understand the risk of malaria in specific regions and take appropriate antimalarial medications. Sleep under bed nets and use insect repellents.
- Dengue Fever: Implement measures to prevent mosquito bites, as there is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue fever.
- Tropical Parasitic Infections: Be aware of diseases like schistosomiasis and filariasis, which are prevalent in some tropical areas. Avoid swimming in freshwater bodies where these parasites may be present.
4. Vaccine-Preventable Diseases:
- Routine Vaccinations: Ensure that routine vaccinations, including those for measles, mumps, rubella, tetanus, and hepatitis, are up to date.
- Specific Tropical Vaccines: Depending on the destination, consider vaccines for diseases like yellow fever or Japanese encephalitis.
5. Respiratory Illnesses:
- Air Quality: Tropical regions may experience poor air quality due to factors like pollution or wildfires. Individuals with respiratory conditions should take precautions, and wearing masks may be advisable in certain situations.
6. Traveler's Diarrhea:
- Contaminated Food: Be cautious about consuming street food or uncooked seafood. Use proper hand hygiene and consider bringing oral rehydration solutions for fluid replacement in case of diarrhea.
7. Sun-Related Health Issues:
- Sunburn and Heatstroke: The intense tropical sun can lead to sunburn and heat-related illnesses. Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and stay hydrated.
- Infectious Skin Conditions: Humid environments can contribute to skin infections. Practice good hygiene and seek prompt medical attention for any skin issues.
8. Pre-Existing Health Conditions:
- Adaptation: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions should work with healthcare professionals to adapt to the tropical environment. This may include adjusting medication dosages or considering potential exacerbations of certain conditions.
9. Local Healthcare Accessibility:
- Medical Facilities: Research the availability and quality of medical facilities at the destination. Identify hospitals and clinics that can provide adequate care in case of emergencies.
- Travel Insurance: Ensure you have comprehensive travel insurance that covers medical emergencies and evacuation if needed.
10. Cultural and Behavioral Considerations:
- Local Practices: Understand local health practices and cultural norms related to hygiene and healthcare. Respect local customs and take necessary precautions.
A thorough Health Risk Analysis is essential for anyone traveling to or residing in tropical regions. This proactive approach involves understanding the specific health risks associated with the environment, taking preventive measures, and being prepared for potential health challenges. By staying informed and adopting appropriate precautions, individuals can mitigate the risks and enjoy a safer and healthier experience in tropical climates.
Medical Emergencies
Preparedness for facing medical emergencies in unusual environments is essential for ensuring the well-being of individuals in diverse settings. Unusual environments, which may include remote areas, adventure travel, or locations with limited medical facilities, present unique challenges when it comes to health issues. Here's a detailed exploration of the strategies and considerations for being prepared to handle medical emergencies in such unusual environments:
1. Risk Assessment and Planning:
- Understanding the Environment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the unusual environment. Identify potential health risks specific to the location, such as extreme weather conditions, wildlife hazards, or geographical challenges.
- Emergency Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive emergency response plan tailored to the identified risks. This plan should include communication protocols, evacuation routes, and the location of the nearest medical facilities.
2. First Aid Training:
- Basic First Aid: Ensure that individuals in the unusual environment have basic first aid training. This includes knowledge of CPR, wound care, and the ability to respond to common medical issues.
- Specialized Training: In environments with specific risks, such as wilderness areas, consider specialized training like wilderness first aid. This equips individuals to handle emergencies in remote locations where professional medical help may be delayed.
3. Emergency Medical Supplies:
- Medical Kits: Pack a well-equipped medical kit containing essential supplies such as bandages, antiseptics, pain relievers, and any necessary prescription medications.
- Specialized Equipment: Consider the unique needs of the environment. For example, in wilderness settings, items like snakebite kits, insect repellent, and emergency blankets may be crucial.
4. Communication Devices:
- Emergency Communication: Ensure access to reliable communication devices, such as satellite phones or emergency radios. In remote areas, standard cell phones may not have coverage.
- Emergency Contact Information: Maintain a list of emergency contacts and relevant medical information for each individual. This information should be easily accessible in case of an emergency.
5. Evacuation Planning:
- Evacuation Routes: Identify and communicate evacuation routes in advance. Know the location of nearby medical facilities and evacuation points.
- Transportation Options: Consider the availability of transportation in the unusual environment. In some cases, evacuation may require unconventional means, such as air transport or specialized vehicles.
6. Adaptability and Resourcefulness:
- Quick Thinking: Encourage a mindset of adaptability and quick thinking in the face of unexpected medical emergencies. Individuals should be prepared to assess situations and make informed decisions.
- Resource Utilization: Learn to make the most of available resources. This may involve improvising medical tools or using the environment to provide support in emergency situations.
7. Environmental Considerations:
- Climate and Altitude: Consider the impact of climate and altitude on health. Individuals traveling to high-altitude locations should be aware of altitude sickness symptoms, while those in extreme climates should take precautions against heat or cold-related issues.
- Water Safety: Ensure access to safe drinking water, as waterborne illnesses can pose a significant threat in unusual environments.
8. Remote Medical Support:
- Telemedicine Services: Explore the availability of telemedicine services for remote medical consultations. In some cases, healthcare professionals can provide guidance and support via video or phone calls.
- Emergency Hotlines: Be aware of local and international emergency hotlines. In the event of a medical emergency, these hotlines can provide guidance and facilitate communication with medical professionals.
9. Community Education:
- Pre-Trip Briefings: Conduct pre-trip briefings to educate individuals about potential health risks and the emergency plan. Ensure everyone is familiar with the location of emergency supplies and evacuation procedures.
- Training Updates: Periodically update first aid training and emergency response plans to address evolving circumstances and risks.
10. Legal and Ethical Considerations:
- Legal Protocols: Understand the legal implications of providing medical assistance in different environments. Be aware of local regulations and protocols regarding emergency care.
- Informed Consent: When providing medical aid, prioritize obtaining informed consent when possible. Communicate clearly with affected individuals or their representatives about the proposed interventions.
Preparedness for medical emergencies in unusual environments demands a proactive and comprehensive approach. By assessing risks, providing training, maintaining communication, and considering the unique challenges of the environment, individuals can enhance their ability to respond effectively to health issues, ensuring a higher likelihood of positive outcomes in challenging circumstances.
In conclusion
adhering to preventive measures against tropical diseases is crucial for maintaining health and safety during travel to these unique regions. Following preventive measures such as receiving appropriate vaccinations, using mosquito repellents, and practicing personal hygiene allows travelers to reduce the risk of contracting infectious diseases. This commitment reflects a deep understanding of the importance of public health and individual responsibility. Therefore, travelers can enjoy their experiences safely and with peace of mind, confident in the preventive measures that protect them from negative health impacts in these distinctive tropical areas.
Sources
What's Your Reaction?