How to regulate blood sugar levels through diet
Achieving blood sugar regulation requires following a balanced diet that includes reducing intake of simple carbohydrates and saturated fats, increasing consumption of fiber and proteins, while monitoring portion sizes and consuming foods with low glycemic index.
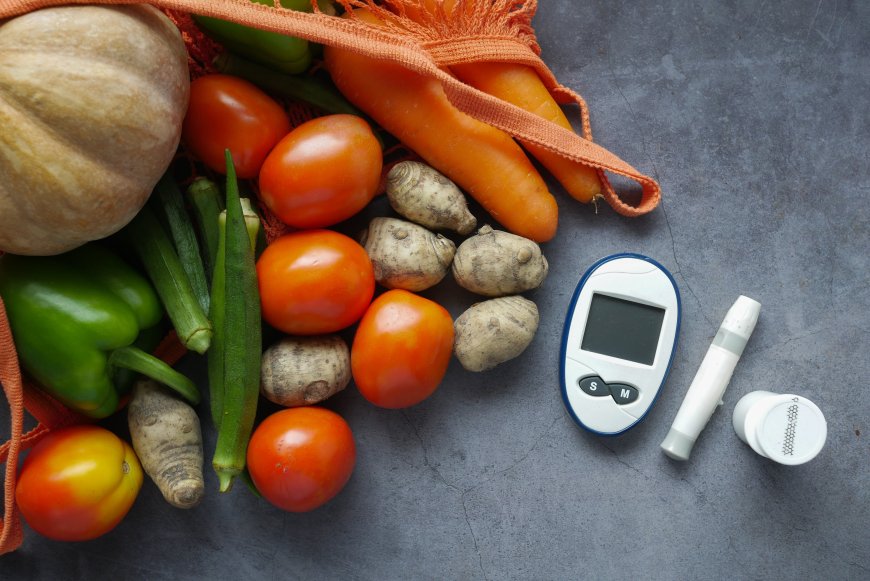
Achieving blood sugar regulation requires following a balanced diet that includes reducing intake of simple carbohydrates and saturated fats, increasing consumption of fiber and proteins, while monitoring portion sizes and consuming foods with low glycemic index.
How to regulate blood sugar levels through diet
Understanding the basics of blood sugar involves comprehending the process of carbohydrate breakdown in the body into simple sugars like glucose, and how they are utilized as a source of energy. Blood sugar levels are significantly influenced by the quality and quantity of food consumed, with excessive intake of carbohydrates and simple sugars considered a primary source of elevated blood sugar levels. Conversely, dietary fiber and proteins contain properties that aid in blood sugar control by slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates and reducing fluctuations in sugar levels. Therefore, regulating blood sugar levels can be achieved by managing the quality and quantity of food intake, necessitating adherence to a balanced diet containing appropriate amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fiber, which promote stability in blood sugar levels.
Identifying appropriate carbohydrates to maintain blood sugar control
Identifying the appropriate carbohydrates to maintain blood sugar control requires understanding the differences between simple and complex carbohydrates, as carbohydrate intake directly affects blood sugar levels. It is preferable to consume complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits with skin, which contain dietary fiber and are slowly digested in the digestive system, helping to prevent a sharp rise in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, it is advised to avoid simple carbohydrates such as refined sugars and white pastries, which are quickly absorbed by the body, leading to a sudden increase in blood sugar levels. Therefore, it is important for individuals struggling with blood sugar regulation issues to identify suitable carbohydrates and follow a diet containing moderate amounts of complex carbohydrates while reducing intake of simple carbohydrates.
The importance of dietary fiber in regulating blood sugar levels
The importance of dietary fiber in regulating blood sugar levels lies in its ability to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and the absorption of sugar in the digestive system. Dietary fiber possesses properties that aid in improving bowel movements and passing food slowly through the digestive tract, meaning that sugar is absorbed more slowly into the bloodstream. This effect reduces fluctuations in blood sugar levels and helps maintain long-term stability.
Furthermore, fiber works to increase satiety and the feeling of fullness, reducing the desire to consume large amounts of food and thus preventing sharp declines in sugar levels after meals. Vegetables, fruits, and whole grains are rich sources of fiber and should be regularly included in the diet to assist in blood sugar regulation.
Overall, consuming adequate amounts of dietary fiber is an essential part of a strategy to regulate blood sugar levels and can contribute to overall health maintenance and prevention of chronic diseases such as diabetes.
The best proteins for achieving blood sugar stability
The best proteins for achieving blood sugar stability include plant-based proteins such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, as they contain high levels of protein and fiber, meaning they digest slowly in the digestive system and help prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, fish, poultry, and eggs are considered healthy protein sources that can be included in the diet to regulate blood sugar levels, as animal proteins provide valuable nutrition and help in feeling full for longer periods.
Furthermore, dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese are good sources of protein and also contain calcium and other essential vitamins. Choosing low-fat varieties is preferred to reduce saturated fats, which can negatively impact heart health.
Overall, including diverse sources of protein in the diet is important for achieving blood sugar stability and effectively regulating its levels. Diversity in protein sources also helps ensure a varied array of other essential nutrients for good health.
Basics of Fat Consumption and Its Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
The basics of fat consumption and its impact on blood sugar levels involve the necessity of choosing healthy fats and reducing saturated and trans fats. Healthy fats such as unsaturated fats found in fatty fish like salmon and tuna, as well as in nuts, chia seeds, and olive oil, contribute to improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of high blood sugar levels. On the other hand, saturated fats found in foods such as fatty meats and full-fat dairy products can lead to increased levels of harmful cholesterol and reduced insulin sensitivity.
Additionally, reducing intake of trans fats and monounsaturated fats, which are typically found in fast food, pastries, and sweets, should be emphasized, as they can increase the risk of obesity and disruptions in blood sugar levels.
Overall, it is important for blood sugar regulation to regularly include healthy fats in the diet, while minimizing harmful and saturated fats as much as possible, in order to achieve a balanced and healthy dietary pattern and ensure long-term health.
Planning healthy meals to control blood sugar regulation
Planning healthy meals to control blood sugar regulation requires considering the balance between carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, while focusing on selecting foods that positively impact blood sugar levels. It is preferable to consume small, frequent meals throughout the day rather than large, infrequent meals, as this can help prevent sudden spikes in sugar levels.
Including healthy protein sources such as grilled chicken, fish, and legumes in your meals can help achieve longer-lasting satiety and reduce fluctuations in sugar levels. Additionally, opting for high-fiber carbohydrates like leafy vegetables and whole grains, while avoiding simple carbohydrates such as added sugars and processed white products, is advisable.
Pre-planning meals and smart shopping for healthy ingredients can contribute to achieving blood sugar control and help maintain good health and stable energy levels throughout the day.
Monitoring glycemic index and adjusting the diet
Monitoring glycemic index and adjusting the diet are essential components of managing blood sugar control. Individuals with blood sugar disorders should regularly monitor their glycemic index, which estimates the average blood sugar level over a specified period, such as three months.
Based on glycemic index monitoring results, dietary adjustments and modifications can be made to achieve better control of blood sugar levels. Foods and meals that negatively or positively impact blood sugar levels can be identified, and carbohydrate, fat, and protein ratios in the diet can be adjusted accordingly.
For example, if the glycemic index is high, it may be appropriate to reduce consumption of simple carbohydrates and sugars while increasing intake of high-fiber carbohydrates, such as vegetables and whole grains. It is also preferable to reduce intake of saturated fats and increase consumption of healthy unsaturated fats.
By employing these strategies, individuals can better regulate blood sugar levels and maintain their overall health. However, individuals should always consult with a doctor or nutrition specialist for personalized and suitable guidance tailored to their individual health condition.
Summary
Regulating blood sugar levels through diet requires following a balanced diet aimed at controlling sugar levels. It is advisable to reduce consumption of simple carbohydrates and added sugars, and increase intake of high-fiber carbohydrates such as vegetables and whole grains. Additionally, reducing saturated fats and increasing consumption of healthy fats is recommended. Regular monitoring of the glycemic index and adjusting the diet based on the results are necessary to achieve better control of blood sugar levels, while ensuring consultation with a doctor or nutrition specialist for appropriate guidance.
Sources
1. American Diabetes Association
2. Harvard University Diabetes Center
3. World Health Organization (WHO)
4. Mayo Clinic
What's Your Reaction?






































































































































































